Food has always been an integral part of human existence, providing not only sustenance but also moments of joy and connection. Over the centuries, our approach to food has evolved alongside technological advancements, from the invention of cooking methods to the rise of industrialized food production. Today, we stand on the brink of a revolution in how we grow, prepare, consume, and even think about food, thanks to the rapid advancement of technology. From the farms that grow our crops to the kitchens where we prepare our meals, technology is making food smarter, more sustainable, and more personalized.
In this article, we will explore how technology is transforming the food landscape and discuss the various innovations that are reshaping the way we interact with food. These changes promise to address many of the challenges we face today, including food security, waste reduction, health concerns, and the environmental impact of traditional food production.
The Digital Revolution in Agriculture
One of the most significant advancements in food technology is occurring in the field of agriculture. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food is expected to rise dramatically. However, traditional farming methods are often inefficient, labor-intensive, and can have negative environmental impacts. Fortunately, technology is helping to transform agriculture into a more efficient, sustainable, and even “smarter” industry.
Precision Farming
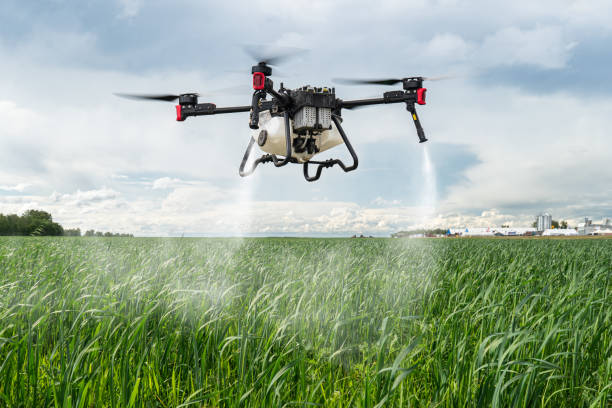
Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture, is revolutionizing the way we grow crops. It involves using advanced technologies, such as GPS, sensors, and drones, to gather real-time data about soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. This data allows farmers to make more informed decisions about when to plant, irrigate, fertilize, and harvest their crops, leading to higher yields and more efficient use of resources.
For example, GPS-guided tractors can plant seeds with pinpoint accuracy, reducing the need for extra fertilizer and pesticide. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors can fly over fields to monitor crop health, allowing farmers to detect pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies early, before they become major problems. This technology not only improves the quality and quantity of crops but also minimizes waste and reduces the environmental impact of farming.
Autonomous Machinery
Another exciting development in agricultural technology is the rise of autonomous machinery. From self-driving tractors to robotic harvesters, automation is making farming more efficient and reducing the reliance on manual labor. These machines can work around the clock, performing tasks like planting, irrigating, and harvesting without human intervention. This not only saves time and money but also helps address labor shortages in agriculture.
For instance, autonomous harvesters are able to identify when a crop is ready to be picked and can harvest it with incredible precision, reducing the chances of damaging the plant or wasting produce. This level of efficiency is crucial in an industry where every ounce of produce counts, and it also helps reduce food waste, which is a significant issue in the global food system.
Vertical Farming and Hydroponics
As urbanization increases, traditional farming is becoming less feasible in some areas. Vertical farming and hydroponics are two innovative solutions that are changing the way we think about food production. Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled indoor environments. This method allows for more efficient use of space, water, and nutrients, making it ideal for urban areas where land is limited.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, is a method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in water. This technique eliminates the need for large expanses of arable land and reduces the environmental impact of traditional farming. Both vertical farming and hydroponics rely heavily on technology, including sensors and artificial intelligence (AI), to monitor and optimize growing conditions, ensuring that plants receive the ideal amounts of light, water, and nutrients.
Genetic Engineering and CRISPR
Genetic engineering has also made its mark on agriculture, enabling scientists to create crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. One of the most promising advancements in this field is the use of CRISPR technology, which allows for precise editing of an organism’s DNA. This technology has the potential to create crops that are not only more resilient but also more nutritious, with enhanced levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
For example, genetically modified (GM) crops such as drought-resistant corn and pest-resistant cotton are already being grown in various parts of the world, helping to ensure a stable food supply despite changing climate conditions. CRISPR could take this technology even further, enabling the development of crops with improved taste, texture, and nutritional content.
Smart Food Manufacturing and Processing
Once crops are harvested, the next stage of food production involves processing and manufacturing. Technology is also playing a major role in improving the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of food manufacturing.
Automation in Food Processing
The food processing industry has embraced automation to streamline operations and increase efficiency. Robots are increasingly used in tasks such as sorting, packaging, and quality control. These machines can work quickly and accurately, reducing the need for human labor and minimizing the risk of contamination or errors.
For example, robots are now being used to package fresh produce, such as fruits and vegetables, with greater speed and precision than ever before. They can also inspect products for defects or contaminants, ensuring that only the highest-quality items make it to market. This not only improves the quality of the food but also helps reduce waste and prevent costly recalls.
Blockchain for Food Traceability
Blockchain technology, which is best known for its association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is also making its way into the food industry. One of the key applications of blockchain in food production is traceability. By using blockchain, food producers can create a digital ledger that tracks the journey of food products from farm to table. This ensures that consumers can verify the origin of their food, as well as its quality and safety.
For example, a consumer could use a smartphone app to scan a QR code on a food package and access detailed information about where the food came from, how it was produced, and whether it meets certain quality standards. This transparency not only helps ensure food safety but also fosters trust between producers and consumers.
Sustainable Packaging
The issue of food packaging has become increasingly important in recent years, as the environmental impact of plastic waste continues to grow. Technology is helping to address this problem by developing innovative, sustainable packaging solutions. Biodegradable packaging made from plant-based materials, such as seaweed and corn starch, is gaining popularity as an alternative to traditional plastic.
Moreover, AI is being used to optimize packaging designs, reducing material usage while maintaining the integrity and safety of the food. Smart packaging, which can monitor the freshness of food and alert consumers when a product is nearing its expiration date, is also becoming more common. These technologies not only reduce waste but also contribute to a more sustainable food system.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics are playing an increasingly important role in making food smarter. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI systems can identify patterns and trends that humans might overlook, helping to optimize every step of the food production process.
Personalized Nutrition
One of the most exciting applications of AI in the food industry is personalized nutrition. With the help of AI, companies can create customized meal plans and food products tailored to an individual’s specific dietary needs, preferences, and health goals. By analyzing data such as genetic information, lifestyle habits, and health conditions, AI can recommend foods that will help improve a person’s overall well-being.
For example, AI-powered apps can analyze a person’s daily food intake and suggest healthier alternatives or supplements to address nutritional deficiencies. Similarly, AI can help individuals with specific dietary requirements, such as those with food allergies, intolerances, or chronic health conditions like diabetes, by recommending foods that meet their unique needs.
AI in Food Safety and Quality Control
AI is also transforming food safety and quality control. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to detect anomalies in food production, such as the presence of harmful bacteria or contaminants. These algorithms can analyze data from sensors, cameras, and other monitoring devices to identify potential risks before they become serious issues.
For example, AI-powered systems can monitor the temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors in food storage and processing facilities, ensuring that products are kept in optimal conditions. AI can also be used to analyze food samples for contaminants, reducing the need for time-consuming and expensive manual testing.
Food Waste Reduction
Food waste is a massive global issue, with approximately one-third of all food produced globally being wasted each year. Technology, particularly AI and data analytics, is helping to tackle this problem by predicting food demand more accurately and optimizing supply chains.
AI algorithms can analyze consumer buying patterns and predict demand for specific food products, reducing overproduction and excess waste. Smart inventory management systems can track the shelf life of food items in stores, ensuring that products are sold before they expire. Additionally, AI-powered apps can help consumers reduce food waste by suggesting recipes based on the ingredients they have at home, helping to prevent food from being thrown away.
The Future of Smart Food
As we look to the future, the potential for technology to make food smarter is limitless. The integration of emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, and virtual reality (VR), will further enhance the way we produce, consume, and interact with food.
IoT in the Kitchen
The Internet of Things (IoT) is already making its way into the kitchen, with smart appliances that can communicate with each other and with users. Smart refrigerators can track the contents inside and alert users when food is running low or nearing its expiration date. Smart ovens can adjust cooking times and temperatures based on the type of food being prepared, ensuring that meals are cooked to perfection every time.
In the future, IoT devices could work together to create a fully automated kitchen, where ingredients are prepared, cooked, and served without the need for human intervention. This could revolutionize the way we think about cooking, making it easier, faster, and more efficient.
3D Food Printing
3D printing technology has already been used to create everything from prosthetics to jewelry, and now it’s making its way into the food industry. 3D food printers can create intricate shapes and designs out of various food ingredients, allowing chefs and home cooks to produce highly personalized meals.
This technology has the potential to change the way we think about food production, enabling the creation of customized meals that cater to individual tastes, dietary restrictions, and nutritional needs. It could also play a significant role in reducing food waste by utilizing ingredients that would otherwise be discarded and turning them into innovative dishes.
Conclusion
Technology is fundamentally transforming the way we produce, process, and consume food, making it smarter, more sustainable, and more personalized. From precision farming to AI-powered nutrition apps, technological innovations are addressing some of the most pressing challenges facing the food industry today. As these technologies continue to evolve, the future of food looks brighter than ever, promising a more efficient, healthier, and sustainable food system for generations to come.