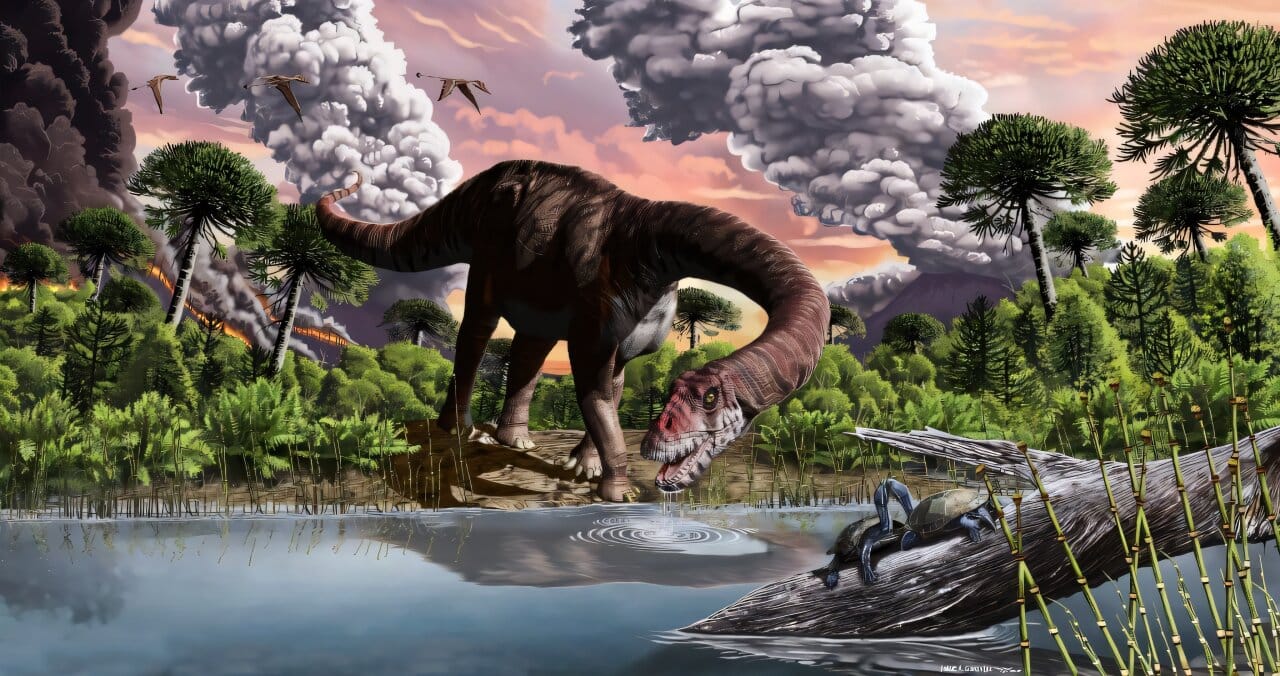
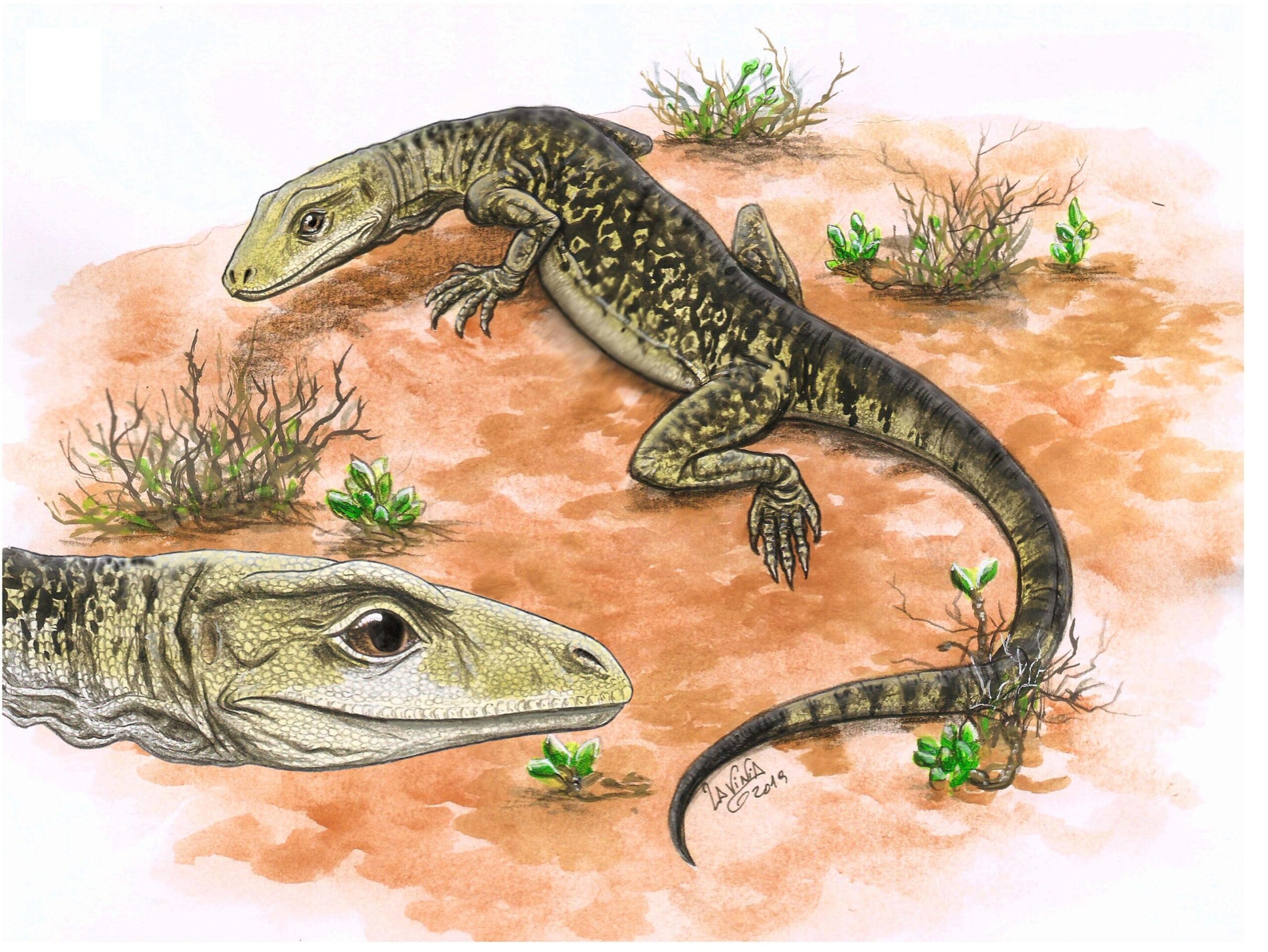
Ancient Feces Reveal How Dinosaurs Came to Rule the Earth
Feces, vomit, and fossilized food remnants from inside the stomachs of ancient animals are often overlooked as mundane byproducts of life, yet they can hold vital clues to our understanding of ancient ecosystems. These seemingly unremarkable substances have now provided fresh insights into one of the most pivotal events in Earth’s history—the rise of the … Read more