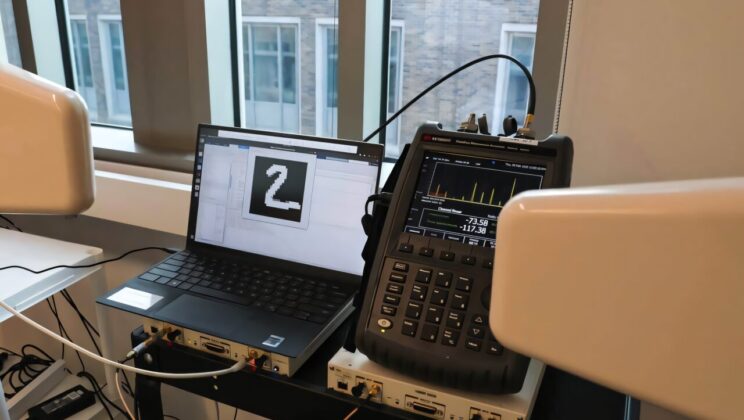
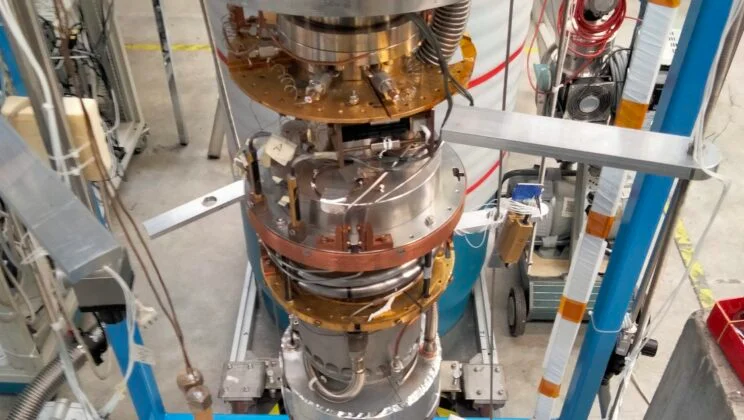
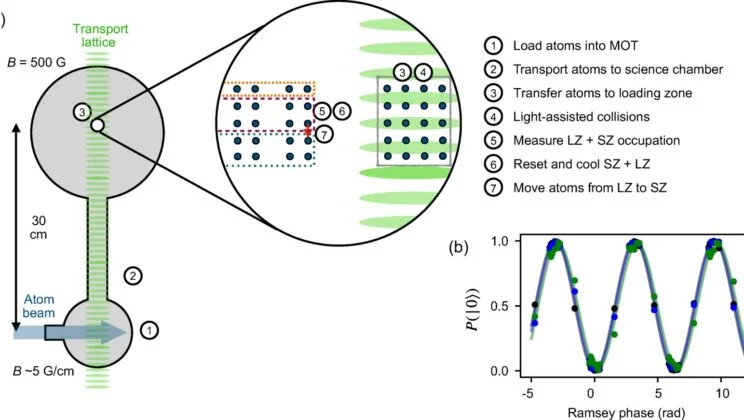
For years, a particular promise shimmered at the edge of modern physics: the idea that tiny electronic devices could unlock…
Category: Physics
Physicists Found a Way to Turn Ordinary Household Light Into a Laser
For as long as humans have learned to harness fire, one question has quietly followed every technological leap: how do…
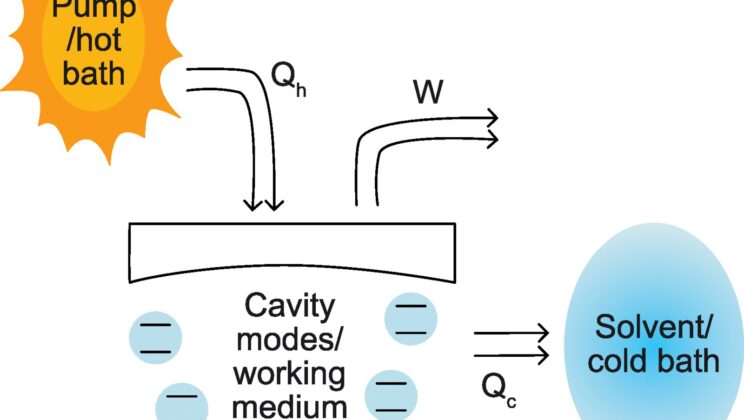
Physicists Created a Strange New Form of Light That Refuses to Fade
For decades, physicists have imagined a strange kind of light that behaves less like a fleeting flash and more like…
Scientists Found a Way to Beam Artificial Intelligence Through the Air Like Radio
The quiet revolution in modern technology is not happening in distant data centers humming with servers. It is happening at…
The Messy Interactions Once Thought to Ruin Quantum Computers Might Actually Be Their Greatest Strength
In the silent, microscopic world of quantum particles, individuality is often a recipe for weakness. A single particle, flickering in…
This Quantum Speed Dating Discovery Could Change How We Build Solar Panels
In the tiny, unseen landscapes of quantum materials, particles lead surprisingly complex social lives. Their behavior is often dictated by…
This New Density Free Regime Could Be the Secret to Limitless Clean Energy
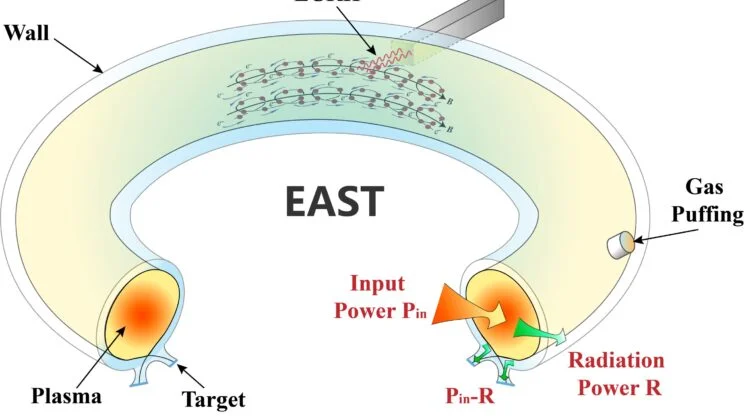
Deep within the circular, metallic heart of a machine known as the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak, or EAST, a miniature…
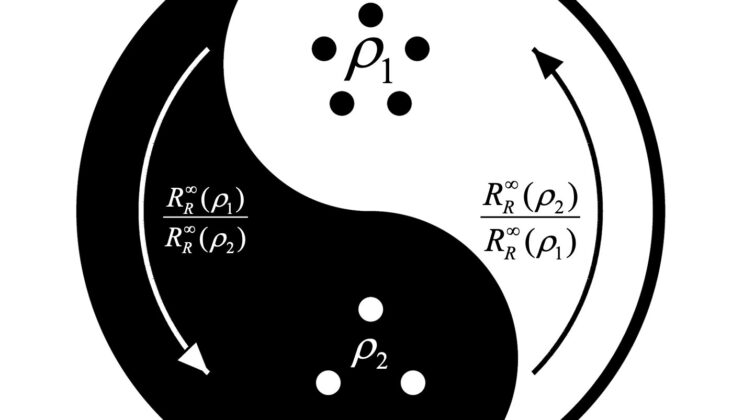
The “Quantum Second Law” Was Resting on a Lie—Until Now
For years, a particular mathematical statement sat quietly at the foundation of quantum information theory, rarely questioned and widely relied…
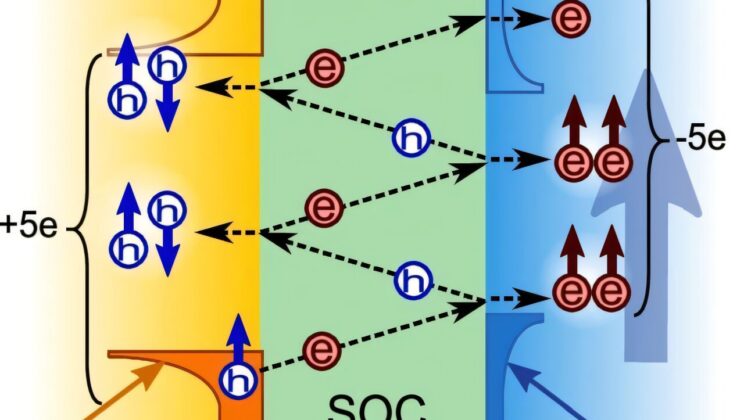
Scientists Observed a “Quantum Conversation” Between Two Materials That Should Be Enemies
Separate two superconductors with a thin barrier, and physics does something quietly astonishing. The property that allows electricity to flow…
Quantum Computers Are Finally Fixing Their Own Mistakes, and the Results Are 70x Better
Quantum computers are often described as machines of the future, but in reality they already exist, humming quietly in laboratories,…
Scientists Turn Extreme Cold and Powerful Magnets Into a New Way to Listen for Dark Matter
The story begins with something that has never been seen. Dark matter does not glow, does not reflect, and does…
Scientists Finally Built Einstein’s “Impossible” Experiment—And the Result Is Not What He Hoped
Nearly a century ago, Albert Einstein sketched an experiment in his mind with the quiet confidence of someone certain he…
This Magnetic “Cloak” Could Hide Devices From Forces That Normally Destroy Them
For centuries, invisibility belonged to myths and imagination. It lived in stories of magic rings and hidden realms, far from…
When Atoms Vanish, This Quantum Computer Doesn’t Stop — It Repairs Itself
Every computer, no matter how advanced, shares a humble vulnerability: parts can fail. In ordinary machines, a broken component can…
Scientists Uncover Why Matter Stops Resisting Heat at Absolute Zero
Imagine a universe where heat no longer flows, where atoms quiver less and less until their restless dance finally halts.…
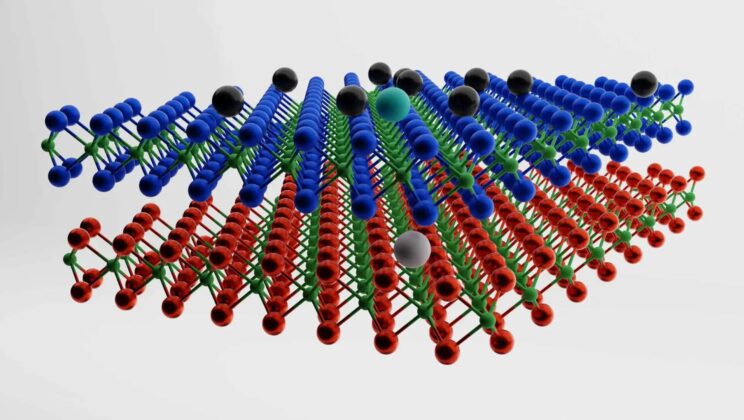
Scientists Discover Ultra-Thin Crystal That Can Bend UV Light in Ways Never Seen Before
Light is usually a stubborn traveler. It bends when it must and speeds along when it can, but its behavior…
Scientists Build Superconducting Amplifier That Makes Backward Waves Disappear
In the world of microwave engineering, silence is sometimes more valuable than sound. Signals at the edge of detection, whisper-quiet…
Scientists Build a “Quantum Antenna” That Sees the Invisible Terahertz World for the First Time
For decades, the terahertz range of the electromagnetic spectrum has been a kind of scientific no-man’s land. It sits quietly…
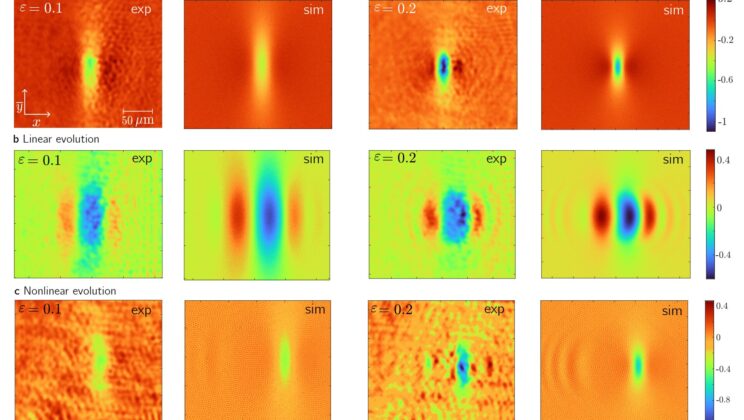
Forget 1s and 0s: This New Light Tech Could Carry ‘Enormous’ Information Per Photon
The story begins with a simple but bold idea. What if light could be shaped so precisely in space and…
The Coldest Stars in Space May Be Exposing a Hidden Force of Nature
Neutron stars are some of the strangest objects in the universe, the ultra-dense remnants left behind after massive stars explode.…
Higgs Boson Sends New Signal at CERN and It’s Pointing Straight at the Muon
For more than a decade, the Higgs boson has stood at the center of one of physics’ greatest stories. First…
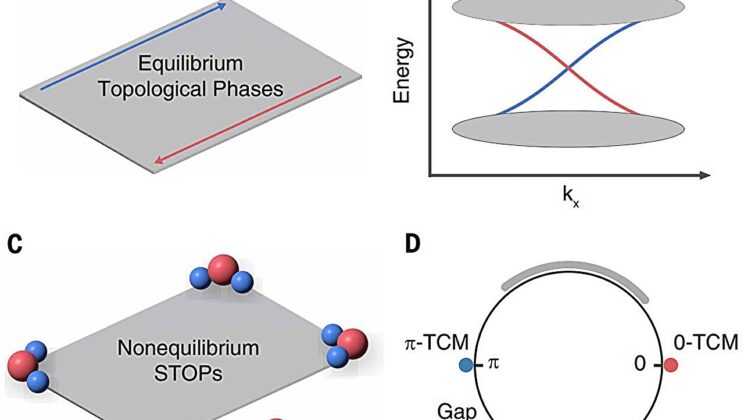
Scientists Unlock the Secret to Super-Stable Quantum Matter—And It’s Hiding in the Corners!
In a small but powerful laboratory hidden deep inside a quantum computer, a groundbreaking experiment was unfolding. It was not…